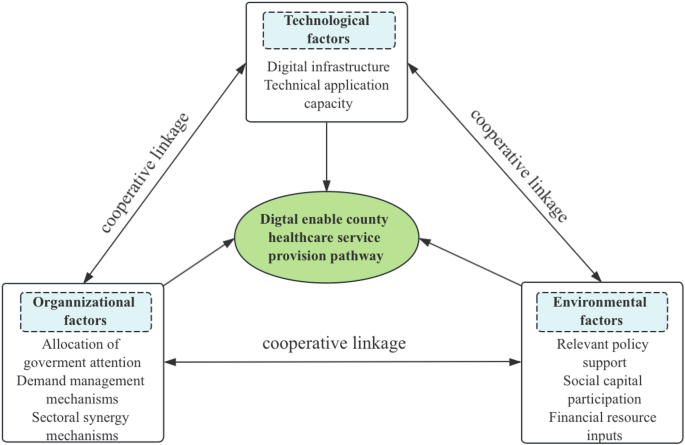
Exploring the pathways of digital technology driven healthcare service delivery in county-level regions
Data calibration
Prior to conducting the univariate necessity analysis, the data must undergo calibration. This process involves assigning set membership values to each case, with the calibrated dataset ranging between 0 and 134. Currently, the two commonly used calibration anchors in academia are 0.75, 0.5, and 0.25; 0.95, 0.5, and 0.05. Generally, researchers should comprehensively select suitable anchors based on their research topic and research content. Existing studies have shown that 0.95, 0.5 and 0.05 anchors have better explanatory power and calibration effect35. Therefore, in conjunction with the research theme, this paper also selects 0.95, 0.5 and 0.05 anchors for data calibration. Of note, the outcome variables and condition variables in this paper, such as technology application capacity, data utilization and sharing, government attention allocation, demand management mechanism, sectoral synergy mechanism, and social capital participation, are 0/1 dichotomous variables, and therefore do not require calibration. The calibration results for the fully affiliated, intersection and fully unaffiliated of the condition variables digital infrastructure 15.35, 10, and 5, respectively. The corresponding policy support was 8, 5, and 2.15, respectively; and the financial resources input was 800.65, 530, and 120.35, respectively. Data collection was processed using Excel software and data analysis was conducted utilizing the fsQCA 3.0 software.
Univariate necessity analysis
Prior to conducting the condition grouping analysis, a univariate necessity analysis was performed following data calibration. Data shown in Table 1 indicates that the consistency scores for all variables were below the 0.9 threshold, indicating that none met the criteria for necessary conditions for either high or low levels of county-level medical service digitalization. This result indicated that there was no single condition in the process of digitally enabled county medical service supply, and that the improvement of the effectiveness of digitally enabled county medical service supply is the result of the joint action of multiple elements (i.e., technology, organization and environment). Therefore, it is necessary to conduct a more in-depth analysis of the different configurations of condition variables using various combinatorial approaches. The results of the necessity analysis of individual variables are shown in Table 1.
Truth table construction
The truth table was developed using the univariate necessary condition analysis results. Briefly, fsQCA3.0 software was applied used to calculate the truth table. According to the algorithm rules of fsQCA3.0 software, if the required result is greater than 0.5, it is assigned as “1”, otherwise it is assigned as “0”. The result variable is set to Y, and the truth table can be obtained after deleting the combination of conditions without case configuration. In this study, SC, JY, SL, ZL, XG, BX, ZB, SJ, CJ represent digital infrastructure, technical application capacity, data utilization and sharing, government attention allocation, demand management mechanism, sectoral synergy mechanism, related policy support, social capital participation, and financial resources input, respectively. The results of the truth table are shown in Table 2.
Analysis of conditional grouping
Data shown in Table 3 revealed four paths that can drive the digitalization of county healthcare service provision in the process of digital empowerment. Each of these columns represents a potential conditional grouping state. These results demonstrated that the consistency of the solutions obtained from the calculation was 0.786, indicating that 78.6% of the actual cases of digital construction of county healthcare service supply that met the four types of conditional groupings had a high level of digitalization of their healthcare service supply. The coverage of the solution was 0.837, suggesting that 83.7% of the cases with a high level of digitization of county healthcare service provision could be explained by these four conditional groupings. The solution’s consistency and coverage exceeded the required threshold, indicating that the analysis was valid. These four grouping paths are sufficient to achieve high digital healthcare service provision at the county level.
Among the conditional groupings of digitally enabled county medical service provision, digital infrastructure can serve as a facilitating factor in the three paths and an inhibiting role in 1 path; technology application capability plays a facilitating role in 2 paths and an inhibitory role in 2 paths; data utilization and sharing plays a facilitating role in 1 path and an inhibitory role in 2 paths; and the allocation of government attention plays a facilitating role in 3 paths and an inhibiting role in 1 path; and the allocation of government attention plays a facilitating role in 3 paths and an inhibitory role in 3 paths and an inhibitory role in 1 path. play a facilitating role in 1 path and a suppressive role in 1 path; demand management mechanisms play a facilitating role in 2 paths and a suppressive role in 1 path; sectoral synergistic mechanisms play a facilitating role in 2 paths and a suppressive role in 1 path; relevant policy support plays a facilitating role in 2 paths and a suppressive role in 2 paths; social capital participation plays a facilitating role; financial resource input exerts a facilitating role in 1 path and a inhibitory role in 1 path.
Based on the findings of the aforementioned analyses, four paths as “technology balance”, “technology-organization”, “organization-environment” and “all-round” are described in this study. Specifically, grouping path 1 indicates that technology application capacity in the county medical service supply has a promoting role, and sectoral synergistic mechanism had a supporting role. This shows that, compared with other conditions, technological conditions are crucial to the improvement of a digitally-enabled county medical service provision. For instance, digital technologies such as artificial intelligence and big data can be essential components in the county medical service provision. It should be noted that coordination of the interactive adaptation of technology, organization and environment is essential to enhance their effectiveness. In this regard, technological conditions (including digital infrastructure, technology application capabilities, and data utilization and sharing) play a central role. Therefore, it is referred to as “technology balanced” in this study. The effectiveness of this approach is based on the principle that successful technological capabilities must be seamlessly integrated with existing organizational processes. A strong digital infrastructure and technological application abilities open up opportunities for enhancing services. However, the absence of departmental coordination mechanisms can lead to data silos and disconnects in processes. In this context, departmental coordination mechanisms function as organizational lubricants, facilitating the smooth integration of technological tools into cross-departmental healthcare service workflows. This transformation turns technological potential into actual operational efficiency and improved service accessibility.
Notably, we obtained a consistency of 0.855 for this path, with a unique coverage of 0.073, and an original coverage of 0.305, indicating that this path explains about 30.5% of the cases of digitally-enabled healthcare service provision in counties, and only 7.3% of the cases can be explained by this path.Pishan County in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region serves as a prime example of this approach. Leveraging an AI-powered medical big data platform, the county has established an information system encompassing 11 subsystems—including medical consortium services, primary care, universal health screenings, and internet hospitals—achieving intelligent integration of medical services across county, township, and village levels. This has significantly enhanced the overall capacity of county-level medical service provision.
The grouping path 2 revels that, when a county has better digital infrastructure and technology application potential in the healthcare service provision, the level of healthcare service provision in the county will be higher if there is a stronger government attention to allocation and establishment of corresponding sectoral synergy mechanisms. Among them, digital infrastructure, data utilization and sharing, government attention allocation and sectoral synergistic mechanisms are key elements of the county medical service supply. Given the significance of technical and organizational conditions in county medical service provision, the path is named “technical-organizational”. This configuration highlights the synergistic effects of “government leadership” and “technology-driven” approaches in the digital empowerment process. Digital infrastructure serves as the foundation, while the utilization and sharing of data represent a qualitative shift from “possessing technology” to “effectively leveraging data,” which requires top-level design. A strong allocation of government attention provides the political momentum and institutional legitimacy necessary to dismantle data barriers and enable integration and sharing. Concurrently, interdepartmental coordination mechanisms translate this high-level attention into concrete, actionable frameworks for cross-agency cooperation. Throughout this process, technological and organizational conditions do not function in isolation; instead, they reinforce one another. Government emphasis on data integration and utilization drives progress, while the realization of data value further strengthens governmental support. This creates a positive feedback loop that collectively enhances robust digital service capabilities.
The consistency coefficient of this path was found to be 0.812, the unique coverage was 0.028, and the original coverage was 0.258. These data demonstrate that this path can explain 25.8% of the cases, however, only 2.8% of the cases can be explained by this path. Deqing County in Guangdong Province exemplifies an effective approach to integrated healthcare. Technologically, Deqing has developed the “Digital Health Deqing Model,” which creates a unified smart health information platform that consolidates data from medical institutions at the county, township, and village levels. This integration facilitates the seamless sharing of residents’ health information throughout their entire lifecycle, effectively breaking down “information silos.” On an organizational level, the county Party committee and government lead collaborative efforts among multiple departments to advance the establishment of medical consortiums. Relevant initiatives are included in annual comprehensive evaluations and supported by a series of policies and management plans. Additionally, a two-tier quality control system and remote collaboration mechanisms have been implemented, enhancing the execution and service capabilities of primary healthcare institutions.
The grouping path 3 shows that government attention allocation, demand management mechanism, and related policy support enhance the process of digitally-enabled county healthcare service provision, while social capital participation and financial resource have supporting roles. Given that the core conditions of this path are organizational and environmental conditions, we termed it as “organizational-environmental” type. This pathway presents a strategic choice for compensating the relatively inadequate technological conditions through robust governance capabilities and a favorable external environment. When a county’s digital technology infrastructure is underdeveloped, increased government attention leads to strategic resource allocation in this sector. Effective demand management mechanisms direct limited resources to areas of greatest need, improving overall resource efficiency. Meanwhile, clear policy support establishes stable and credible expectations, which are essential for attracting social capital and securing fiscal investment. In this context, social capital and fiscal investment are interconnected; they are mobilized through clear policy signals and effective government management.
The essence of this path lies in building a robust “organization-environment” ecosystem that leverages governance and institutional innovation to mobilize and integrate resources, thereby overcoming technological shortcomings. The consistency of this pathway was 1.0, with a unique coverage of 0.039, and the original coverage of 0.037, indicating that this pathway could explain 3.7% of the cases, and only 3.9% of the cases were explained by this pathway. Taojian County in Hunan Province serves as a prime example of this approach. Despite relatively limited local technical resources, the county government actively introduced social capital into healthcare service provision through enhanced policy guidance and institutional development. The county people’s hospital partnered with Dasai Intelligent Technology to implement an AIoT smart IoT platform and a digital logistics management system. These initiatives have elevated hospital management efficiency and operational standards while achieving energy conservation, consumption reduction, and cost savings.
The grouping path 4 shows that technology, organization and environmental conditions synergize to facilitate the digital empowerment of the provision of healthcare services in the county, and hence was named “all-round”. This pathway illustrates the ideal state of mature digital transformation, characterized by a highly coupled and synergistically evolving ecosystem of technological, organizational, and environmental subsystems. In this model, advanced technological infrastructure and capabilities equip organizations with the tools necessary for efficient service delivery. Agile organizational structures, along with sustained governmental attention, ensure these tools are effectively utilized. Meanwhile, comprehensive policy support, diversified funding sources, and proactive demand management work together to create a sustainable, resilient, and responsive external support environment. These elements interact in complex ways, generating synergistic effects rather than following a simple linear relationship. Consequently, this pathway typically requires counties to possess superior comprehensive endowments, reflecting a systemic achievement in the delivery of digital healthcare services.
Notably, the consistency of the path was 0.887, with a unique coverage of 0.119, and original coverage of 0.317, indicating that the path can explained 31.7% of the cases, and 11.9% of the cases were only explained by the path. Changxing County in Zhejiang Province exemplifies this approach through systematic coordination across technological, organizational, and environmental dimensions. Technologically, it builds the “Health Brain” platform to integrate data and generate health profiles for precision services. Organizationally, two major medical consortiums lead the establishment of a three-tiered county-township-village collaborative management system, promoting the integration of medical care and disease prevention. Environmentally, it actively introduces social capital to develop convenient applications like “Zhixiangbao” and provides comprehensive health management services, forming a multi-faceted digital service delivery model.
Robustness testing
To ensure the robustness of the research results, this study conducted two tests. The first test adjusted the consistency threshold from the original 0.8 to 0.85, while the second test raised the PRI consistency from 0.65 to 0.7. Both tests yielded results that were consistent with the original configuration paths. Specifically, the overall consistency increased from 0.786 to 0.805, although the overall coverage decreased from 0.837 to 0.812. These findings indicate that the research results are stable.
link